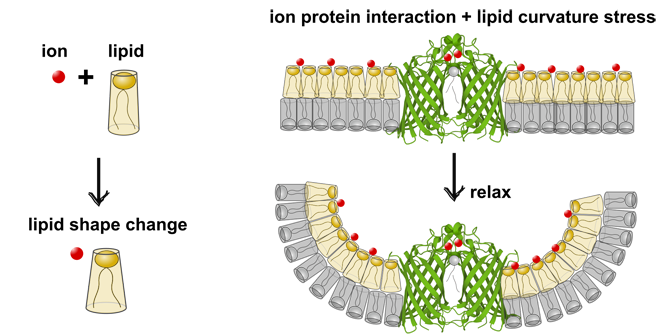
Metal ions are important helpers for proteins. They often ensure that proteins function properly and remain stable. In the case of the enzyme OmpLA (an enzyme in the outer cell membrane of Gram-negative bacteria), calcium ions help it to remain in its active form.
We investigated how OmpLA degrades (hydrolyses) lipids in the membrane. We tested different membranes: electrically neutral and negatively charged and with symmetrical or asymmetrical lipid distribution.
In membranes without charge, OmpLA was more active in symmetrical membranes than in asymmetrical membranes. This is because there are no voltage differences between the two membrane layers. Surprisingly, the opposite was true for charged membranes, where OmpLA was more active in asymmetric membranes.
Small-angle X-ray measurements showed that the shape of the charged lipids changes as soon as calcium is added. This reduces the voltage in asymmetric membranes, which increases enzyme activity. A similar effect also occurs with sodium ions. These influence the lipid shape, but they do not bind directly to the protein.
Our results show that metal ions do not only react directly with membrane proteins. They also influence their activity indirectly by changing the shape of the lipids.
- Link to the article: P. Piller et al, RSC App Interf 2: 69 - 73 (2025) DOI: 10.1039/D4LF00309H.
From: Piller et al, RSC Appl. Interf (2025), Licence: (CC-BY 4.0 DEED)
Overview of important contributions
- P. Piller, P. Reiterer, E.F. Semeraro, & G. Pabst, Metal ion cofactors modulate integral enzyme activity by varying differential membrane curvature stress, RSC App Interf 2: 69 – 73 (2025) DOI: 10.1039/D4LF00309H.
- M.P.K Frewein, P. Piller, E.F. Semeraro, O. Czakkel, Y. Gerelli, L. Porcar & G. Pabst, Distributing aminophospholipids asymmetrically across leaflets causes anomalous membrane stiffening, Biophys. J. 122, 2445 (2023), DOI: 10.1016/j.bpj.2023.04.025.
- P. Piller, E.F. Semeraro, G. N. Rechberger, S. Keller & G. Pabst, Allosteric modulation of integral protein activity by differential stress in asymmetric membranes, PNAS Nexus 2, 1 (2023), DOI: 10.1103/10.1093/pnasnexus/pgad126.
- J. Jennings, & G. Pabst, Multiple routes to bicontinuous cubic liquid crystal phases discovered by high-throughput self-assembly screening of multi-tail lipidoids, Small 2206747 (2023), DOI: 10.1002/smll.202206747.
- E.F. Semeraro, L. Marx, J. Mandl, I. Letofsky-Papst, C. Mayrhofer, M.P.K. Frewein, H.L. Scott, S. Prévost, H. Bergler, K. Lohner & G. Pabst, Lactoferricins impair the cytosolic membrane of Escherichia coli within a few seconds and accumulate inside the cell, eLife 11, e72850 (2022), DOI: 10.1101/2021.09.24.461681.
- M.P.K. Frewein, P. Piller, E.F. Semeraro, K.C. Batchu, F.A. Heberle, H.L. Scott, Y. Gerelli, L. Porcar, and G. Pabst, Interdigitation-induced order and disorder in asymmetric membranes, J Membrane Biol. (2022), DOI: 10.1007/s00232-022-00234-0.
- M. Kaltenegger, J. Kremser, M.P. Frewein, P. Ziherl, D.J. Bonthuis & G. Pabst, Intrinsic lipid curvatures of mammalian plasma membrane outer leaflet lipids and ceramides, Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1836, 183709 (2021), DOI: 10.1016/j.bbamem.2021.183709.
- B. Eicher, D. Marquardt, F.A. Heberle, I. Letofsky-Pabst, G.N. Rechberger, M.-S. Appavou, J. Katsaras & G. Pabst, Intrinsic curvature-mediated transbilayer coupling in asymmetric lipid vesicles, Biophys. J. 114, 146 (2018), DOI: 10.1016/j.bpj.2017.11.009.
- B.-S. Lu, S.P. Gupta, M. Belička, R. Podgornik & G. Pabst, Modulation of elasticity and interactions in charged lipid multibilayers: monovalent salt solutions, Langmuir 32, 1355 (2016), DOI: 10.1021/acs.langmuir.6b03614.
- B. Kollmitzer, P. Heftberger, R. Podgornik, J.F. Nagle & G. Pabst, Bending rigidities and interdomain forces in membranes with coexisting lipid domains Biophys. J. 108, 2833 (2015), DOI: 10.1016/j.bpj.2015.05.003.
- E.F. Semeraro, M.P.K. Frewein, & G. Pabst, Chapter Fourteen - Structure of symmetric and asymmetric lipid membranes from joint SAXS/SANS, in Methods in Enzymol, T. Baumgart, M. Deserno (edts), Academic Press, 700: 349 - 383 (2024) DOI: 10.1016/bs.mie.2024.02.017.
- G. Pabst, & S. Keller, Exploring membrane asymmetry and its effects on membrane proteins, Trends Biochem Sci, 49: 333 -345 (2024) DOI: 10.1016/j.tibs.2024.01.007
- G.J. Schütz & G. Pabst, The asymmetric plasma membrane—A composite material combining different functionalities? BioEssays 45: 2300116 (2023) DOI: 10.1002/bies.202300116
- E.F. Semeraro, L. Marx, M.P.K. Frewein, and G. Pabst. Increasing complexity in small-angle X-ray and neutron scattering experiments: from biological membrane mimics to live cells, Soft Matter 17: 222 - 232 (2021) DOI: 10.1039/C9SM02352F
- D. Marquardt, F.A. Heberle, J.D. Nickels, G. Pabst, & J. Katsaras. On scattered waves and lipid domains: detecting membrane rafts with X-rays and neutrons. Soft Matter 11: 9055 - 9072 (2015). DOI: 10.1039/C5SM01807B
- D. Marquardt, B. Geier, and G. Pabst, Asymmetric lipid membranes: towards more realistic model systems. Membranes 5: 180 - 196 (2015). DOI: 10.3390/membranes5020180
G. Pabst, N. Kučerka, M.-P. Nieh, & J Katsaras (Hg), Liposomes, Lipid Bilayers and Model Membranes From Basic Research to Application, CRC Press (2014) ISBN: 9781138198753